Explore Islam - Complete Guide
Discover the comprehensive teachings of Islam through 7 essential topics. Click on any topic to explore its detailed content below.
Allah – The Creator
6 Topics
Legacy of Revelation and Messengers
6 Topics
The Final Messenger & Final Revelation
9 Topics
The Deen – Islam, Iman, Ihsan
6 Topics
Islamic Lifestyle: Morality, Family, and Society
4 Topics
The Hereafter
7 Topics
How to Become a Muslim
2 Topics
Allah – The Creator
Who is Allah?
Allah is the One and Only true God, the Creator and Sustainer of all existence. He is the Lord of the heavens, the earth, and everything in between — from the vast galaxies to the smallest atom. Allah exists eternally without beginning or end. He is As-Samad (The Eternal, Absolute, Self-Sufficient One) — completely independent of His creation while all creation is utterly dependent upon Him for every moment of existence.
Allah is absolutely unique in His essence, attributes, and actions. He does not resemble His creation in any way. As He declares in the Qur'an: "There is nothing like unto Him, and He is the All-Hearing, All-Seeing" (Qur'an 42:11). He is far above having a body, form, parts, or any deficiency. He was not begotten nor does He beget. He has no parents, spouse, children, or partners — these are characteristics of created beings, and Allah is far above such limitations.
Surah Al-Ikhlas (Chapter 112) comprehensively summarizes this: "Say: He is Allah, [Who is] One. Allah, the Eternal Refuge. He neither begets nor is born. Nor is there to Him any equivalent." The Prophet Muhammad ﷺ said this chapter is equal to one-third of the Qur'an due to its affirmation of Tawheed (pure monotheism). Allah is the First and the Last, the Manifest and the Hidden. He is above His Throne (Al-'Arsh) in a manner befitting His majesty, distinct from His creation, yet His knowledge encompasses all things. He is with His creation by His knowledge, seeing, hearing, and power — not by His essence being everywhere, as this contradicts His transcendence affirmed by Ahl al-Sunnah wal-Jama'ah based on Qur'an 20:5 and other texts.
Names and Attributes of Allah
Allah has revealed to us His Most Beautiful Names (Al-Asma al-Husna) and Perfect Attributes (As-Sifat) through the Qur'an and authentic Sunnah. These names and attributes describe His absolute perfection, majesty, mercy, wisdom, power, and glory. Understanding them is fundamental to knowing Allah and worshipping Him correctly.
Examples of Allah's Names:
Allah says: "And to Allah belong the best names, so invoke Him by them. And leave [the company of] those who practice deviation concerning His names. They will be recompensed for what they have been doing" (Qur'an 7:180).
The Methodology of Ahl al-Sunnah Regarding Allah's Attributes:
The Salaf (righteous predecessors) - the Companions, their students, and those who followed them - established a clear methodology in affirming Allah's attributes:
1. Ithbat (Affirmation): We affirm all the attributes that Allah affirmed for Himself in the Qur'an and that the Prophet Muhammad ﷺ affirmed for Him in authentic hadith — without denial, distortion, asking "how," or resembling them to creation.
2. Tanzeeh (Negating imperfection): We declare Allah free from any imperfection, deficiency, or resemblance to created things. His attributes are perfect and befitting His majesty.
3. Tafweed al-Kayfiyyah (Leaving the "how" to Allah): We do not delve into asking "how" these attributes are, as Imam Malik said regarding Allah's Istawa (rising) over the Throne: "The Istawa is known, the how is unknown, believing in it is obligatory, and asking about it is an innovation."
Practical Implications:
The Prophet ﷺ said: "Allah has ninety-nine names, one hundred minus one. Whoever enumerates them (learns, understands, and acts upon them) will enter Paradise" (Sahih al-Bukhari).
Tawheed and its Three Aspects
Tawheed (the Oneness of Allah) is the foundation, core, and essence of Islam. It is the central message of all prophets from Adam to Muhammad (peace be upon them all). Tawheed is what distinguishes a Muslim from a non-Muslim, and it is the key to Paradise. The scholars have categorized Tawheed into three interconnected aspects to facilitate understanding:
1. Tawheed ar-Rububiyyah (Oneness of Lordship):
This means singling out Allah as the sole Creator, Sustainer, Provider, Controller, and Manager of all affairs. It affirms that:
Allah says: "Indeed, your Lord is Allah, who created the heavens and earth in six days and then established Himself above the Throne. He covers the night with the day, [another night] chasing it rapidly; and [He created] the sun, the moon, and the stars, subjected by His command. Unquestionably, His is the creation and the command; blessed is Allah, Lord of the worlds" (Qur'an 7:54).
Even the polytheists of Makkah acknowledged this aspect of Tawheed. Allah says: "And if you asked them, 'Who created the heavens and earth?' they would surely say, 'Allah'" (Qur'an 39:38). However, this acknowledgment alone did not make them Muslims because they failed in the other categories.
2. Tawheed al-Uluhiyyah/al-'Ibadah (Oneness of Worship):
This is the most important category and the one most commonly violated. It means directing all acts of worship exclusively to Allah alone, without any partners or intermediaries. This includes:
This is what the prophets called people to primarily. The Prophet Muhammad ﷺ spent the first 13 years in Makkah calling to "La ilaha illa Allah" (None has the right to be worshipped except Allah). This testimony means:
Violating this category is shirk (associating partners with Allah), which is the greatest sin. Allah says: "Indeed, Allah does not forgive association with Him, but He forgives what is less than that for whom He wills" (Qur'an 4:48).
3. Tawheed al-Asma was-Sifat (Oneness of Allah's Names and Attributes):
This means affirming for Allah all the names and attributes He affirmed for Himself in the Qur'an and that His Messenger ﷺ affirmed for Him in authentic hadith — in a manner befitting His majesty, without:
We believe Allah has:
The correct methodology is: "There is nothing like unto Him, and He is the All-Hearing, All-Seeing" (Qur'an 42:11). We affirm what Allah affirmed without likening it to creation, and we negate what Allah negated without denying His perfect attributes.
The Interconnection:
These three categories are inseparable. True Tawheed requires:
Deficiency in any category constitutes a deficiency in Tawheed. The testimony "La ilaha illa Allah" encompasses all three: Allah alone is the True God worthy of worship (Uluhiyyah), the Lord and Creator (Rububiyyah), with perfect names and attributes (Asma was-Sifat).
Why Tawheed Matters:
Tawheed liberates humanity from the slavery of false gods, desires, and other people, making them servants only to their Creator.
Allah's Rights Over Us
Allah, as our Creator, Sustainer, and Lord, has rights over us that must be fulfilled. Understanding and implementing these rights is the essence of servitude ('ubudiyyah) and the purpose for which we were created.
The Primary Right - Tawheed (Worship Allah Alone):
The greatest and most fundamental right of Allah upon His creation is that they worship Him alone without associating any partners with Him. This is narrated in the authentic hadith:
Mu'adh ibn Jabal (may Allah be pleased with him) reported that the Prophet ﷺ said: "Do you know what Allah's right upon His servants is?" I said, "Allah and His Messenger know best." He said, "To worship Him alone and not associate anything with Him." Then he asked, "Do you know what the servants' right upon Allah is?" I said, "Allah and His Messenger know best." He said, "That He will not punish anyone who does not associate anything with Him" (Sahih al-Bukhari & Muslim).
This right encompasses:
1. The Shahada (Testimony of Faith): Sincerely testifying and living by "La ilaha illa Allah, Muhammad Rasulullah" — affirming that only Allah deserves worship and Muhammad ﷺ is His final messenger. This must be:
2. All Forms of Worship Exclusively for Allah:
Salah (Prayer): Establishing the five daily prayers at their prescribed times with proper concentration and humility. The Prophet ﷺ said: "The head of the matter is Islam, its pillar is the prayer, and its peak is jihad in the way of Allah" (Tirmidhi - Hasan Sahih).
Dua (Supplication): Calling upon Allah alone for help, guidance, provision, and all needs — not calling upon the dead, absent, or anyone incapable of responding. "And your Lord says: 'Call upon Me; I will respond to you'" (Qur'an 40:60).
Tawakkul (Trust): Placing complete reliance upon Allah while taking appropriate means. "And upon Allah rely, if you should be believers" (Qur'an 5:23).
Khawf and Raja' (Fear and Hope): Maintaining balance between fearing Allah's punishment and hoping for His mercy. "They used to hasten to good deeds and supplicate Us in hope and fear" (Qur'an 21:90).
Mahabbah (Love): Supreme love reserved only for Allah, above all else. "But those who believe are stronger in love for Allah" (Qur'an 2:165).
3. Obedience to Allah's Commands:
4. Gratitude (Shukr): Being thankful for His countless blessings by:
Allah says: "So remember Me; I will remember you. And be grateful to Me and do not deny Me" (Qur'an 2:152).
5. Knowledge of Allah: Learning about Allah through His names, attributes, and commands. The Prophet ﷺ said: "Seeking knowledge is obligatory upon every Muslim" (Ibn Majah - Hasan).
6. Dhikr (Remembrance): Frequently remembering Allah through prescribed dhikr and general remembrance. "So remember Me; I will remember you" (Qur'an 2:152).
7. Repentance (Tawbah): Returning to Allah sincerely when we fall short, fulfilling its conditions:
8. Preferring Allah's Pleasure Over Everything: Prioritizing what pleases Allah over personal desires, customs, family, wealth, or status. "Say: If your fathers, your sons, your brothers, your wives, your relatives, wealth which you have obtained, commerce wherein you fear decline, and dwellings with which you are pleased are more beloved to you than Allah and His Messenger and jihad in His cause, then wait until Allah executes His command" (Qur'an 9:24).
The Servant's Right Upon Allah:
Remarkably, when servants fulfill Allah's rights, Allah out of His generosity has promised them rights upon Him:
However, Allah owes us nothing — these are His gracious promises, not obligations upon Him. He is Al-Ghani (The Self-Sufficient) while we are al-fuqara (the needy ones).
Consequences of Neglecting Allah's Rights:
Practical Application:
Every action in our lives should be:
This transforms even mundane activities (eating, sleeping, working) into acts of worship when done with the right intention and within Islamic guidelines. The believer lives every moment aware that Allah's right is to be obeyed, remembered, and worshipped in all circumstances.
Shirk, Kufr, and Nifaq
Understanding the opposites of Tawheed and Iman is crucial for protecting one's faith and recognizing the boundaries of Islam. These concepts represent the gravest spiritual diseases that destroy faith and lead to eternal punishment if one dies upon them without repentance.
SHIRK (Associating Partners with Allah):
Shirk is the gravest sin in Islam — the opposite of Tawheed. It means associating partners with Allah in any form of worship, lordship, or His names and attributes. Allah says: "Indeed, Allah does not forgive association with Him, but He forgives what is less than that for whom He wills. And he who associates others with Allah has certainly fabricated a tremendous sin" (Qur'an 4:48).
Types of Shirk:
1. Shirk Akbar (Major Shirk) — This expels a person from Islam and results in eternal Hellfire if one dies upon it:
a) Shirk in Worship (Uluhiyyah):
b) Shirk in Lordship (Rububiyyah):
c) Shirk in Names and Attributes:
Examples from our times:
2. Shirk Asghar (Minor Shirk) — This does not expel from Islam but severely damages one's faith and nullifies specific deeds:
The Prophet ﷺ warned: "What I fear most for you is minor shirk." They asked, "What is minor shirk, O Messenger of Allah?" He said, "Showing off" (Ahmad - Sahih).
KUFR (Disbelief):
Kufr means rejecting or disbelieving in Allah, His messengers, His books, or any fundamental aspect of Islam.
Types of Kufr:
1. Kufr Akbar (Major Disbelief) — Expels from Islam:
a) Kufr al-Inkaar (Denial): Rejecting Allah's existence, denying the Prophethood, rejecting the Qur'an, or denying any known fundamental of the religion
b) Kufr al-Istikbaar (Arrogance): Knowing the truth but refusing to accept it out of pride (like Iblis/Satan)
c) Kufr al-Shak (Doubt): Having doubt about Allah, the Messenger, or Islam's fundamentals
d) Kufr al-I'raad (Turning away): Completely neglecting to learn or practice Islam despite being able
e) Kufr an-Nifaq (Hypocrisy): Appearing Muslim outwardly while disbelieving inwardly
Forms that nullify Islam (Nawaqid al-Islam):
2. Kufr Asghar (Minor Disbelief) — Does not expel from Islam but is a major sin:
NIFAQ (Hypocrisy):
Hypocrisy is among the most dangerous diseases of the heart because it combines the appearance of faith with the reality of disbelief.
1. Nifaq Akbar (Major Hypocrisy in Belief):
This is when a person outwardly appears Muslim but inwardly disbelieves. This person is considered a disbeliever in Allah's sight and will be in the lowest level of Hellfire. Allah says: "Indeed, the hypocrites will be in the lowest depths of the Fire - and never will you find for them a helper" (Qur'an 4:145).
Characteristics mentioned in the Qur'an:
Examples:
2. Nifaq Asghar (Minor Hypocrisy in Actions):
This refers to having characteristics of hypocrites in one's behavior while having true faith in the heart. The Prophet ﷺ said: "There are four traits, whoever has them all is a pure hypocrite, and whoever has one of them has a characteristic of hypocrisy until he gives it up: when he speaks, he lies; when he makes a promise, he breaks it; when he makes a covenant, he betrays it; and when he disputes, he behaves in an evil, insulting manner" (Sahih al-Bukhari & Muslim).
Other signs:
Protection from These Diseases:
1. Learn authentic Tawheed from Qur'an and Sunnah 2. Sincerity (Ikhlas) in all actions 3. Following the Sunnah in worship 4. Regular self-accountability (muhasaba) 5. Avoiding innovations (bid'ah) in religion 6. Keeping company of righteous people 7. Frequent repentance (tawbah) 8. Studying the lives of the Sahabah (Companions) 9. Understanding and implementing the conditions of La ilaha illa Allah
These are not mere academic concepts but life-defining realities that determine one's eternal destination. Every Muslim must learn about them to safeguard their faith and achieve salvation.
Verses About Allah
The Qur'an is the speech of Allah, and it is filled with verses that describe His greatness, majesty, mercy, knowledge, power, and wisdom. These verses serve as anchors for our faith, sources of comfort in difficulty, and reminders of Allah's constant presence and care. Reflecting upon them increases iman (faith) and draws the heart closer to Allah.
Allah's Absolute Oneness:
"Say, 'He is Allah, [Who is] One, Allah, the Eternal Refuge. He neither begets nor is born, nor is there to Him any equivalent.'" (Qur'an 112:1-4) This chapter comprehensively summarizes Tawheed in its purest form.
"And your god is one God. There is no deity except Him, the Entirely Merciful, the Especially Merciful." (Qur'an 2:163)
"Allah - there is no deity except Him, the Ever-Living, the Sustainer of existence. Neither drowsiness overtakes Him nor sleep. To Him belongs whatever is in the heavens and whatever is on the earth. Who is it that can intercede with Him except by His permission? He knows what is before them and what will be after them, and they encompass not a thing of His knowledge except for what He wills. His Throne extends over the heavens and the earth, and their preservation tires Him not. And He is the Most High, the Most Great." (Ayat al-Kursi - Qur'an 2:255) The greatest verse in the Qur'an, as stated by the Prophet ﷺ.
Allah's Transcendence and Uniqueness:
"There is nothing like unto Him, and He is the Hearing, the Seeing." (Qur'an 42:11) This verse establishes that Allah is completely unique and incomparable.
"Vision perceives Him not, but He perceives [all] vision; and He is the Subtle, the Acquainted." (Qur'an 6:103)
"The Most Merciful [Who is] above the Throne established." (Qur'an 20:5) Ahl al-Sunnah affirm Allah's Istawa (rising) above the Throne in a manner befitting His majesty.
Allah's Knowledge:
"And with Him are the keys of the unseen; none knows them except Him. And He knows what is on the land and in the sea. Not a leaf falls but that He knows it. And no grain is there within the darknesses of the earth and no moist or dry [thing] but that it is [written] in a clear record." (Qur'an 6:59)
"Indeed, Allah is over all things competent." (Qur'an 2:20)
"Do you not know that Allah knows what is in the heaven and earth? Indeed, that is in a Record. Indeed that, for Allah, is easy." (Qur'an 22:70)
"And He is with you wherever you are. And Allah, of what you do, is Seeing." (Qur'an 57:4) The scholars of Ahl al-Sunnah explain: Allah is with us by His knowledge, seeing, hearing, and power — not by His essence being everywhere, as He is above His Throne, distinct from His creation.
Allah's Mercy:
"And My Mercy encompasses all things." (Qur'an 7:156)
"Say, 'O My servants who have transgressed against themselves, do not despair of the mercy of Allah. Indeed, Allah forgives all sins. Indeed, it is He who is the Forgiving, the Merciful.'" (Qur'an 39:53) This verse gives immense hope to sinners who wish to repent.
"But My mercy overcomes My wrath." (Hadith Qudsi - Sahih al-Bukhari)
Allah's Power and Control:
"Indeed, Allah holds the heavens and the earth, lest they cease. And if they should cease, no one could hold them after Him. Indeed, He is Forbearing and Forgiving." (Qur'an 35:41)
"And to Allah belongs the dominion of the heavens and the earth, and Allah is over all things competent." (Qur'an 3:189)
"The command is entirely [from] Allah." (Qur'an 13:31)
"Is not Allah the most just of judges?" (Qur'an 95:8)
Allah's Watchfulness:
"Indeed, Allah is ever, over you, an Observer." (Qur'an 4:1)
"And Allah is not unaware of what you do." (Qur'an 2:85)
"And fear Allah and know that Allah is Seeing of what you do." (Qur'an 2:233)
"Does he not know that Allah sees?" (Qur'an 96:14)
Allah's Self-Sufficiency:
"O mankind, you are those in need of Allah, while Allah is the Free of need, the Praiseworthy." (Qur'an 35:15)
"And whoever strives only strives for [the benefit of] himself. Indeed, Allah is Free from need of the worlds." (Qur'an 29:6)
Allah's Attributes of Action:
"He creates what He wills." (Qur'an 42:49)
"And Allah speaks the truth, and He guides to the [right] way." (Qur'an 33:4)
"Indeed, your Lord is Allah, who created the heavens and earth in six days and then established Himself above the Throne. He covers the night with the day, [another night] chasing it rapidly; and [He created] the sun, the moon, and the stars, subjected by His command. Unquestionably, His is the creation and the command; blessed is Allah, Lord of the worlds." (Qur'an 7:54)
Allah's Promise and Truthfulness:
"And who is more truthful than Allah in statement?" (Qur'an 4:87)
"Indeed, the promise of Allah is truth." (Qur'an 31:33)
The Promise of Response:
"And when My servants ask you concerning Me - indeed I am near. I respond to the invocation of the supplicant when he calls upon Me. So let them respond to Me and believe in Me that they may be [rightly] guided." (Qur'an 2:186)
Allah's Love and Pleasure:
"Indeed, Allah loves those who are constantly repentant and loves those who purify themselves." (Qur'an 2:222)
"But Allah has endeared to you the faith and has made it pleasing in your hearts and has made hateful to you disbelief, defiance and disobedience. Those are the [rightly] guided." (Qur'an 49:7)
The Greatest Reward:
"[Some] faces, that Day, will be radiant, looking at their Lord." (Qur'an 75:22-23) Ahl al-Sunnah affirm that the believers will see Allah in Paradise with their eyes, a vision befitting His majesty.
Practical Application:
These verses should be:
The more we know Allah through His words, the more we love Him, fear Him appropriately, hope in His mercy, rely upon Him, and find peace and purpose in worshipping Him alone.
Legacy of Revelation and Messengers
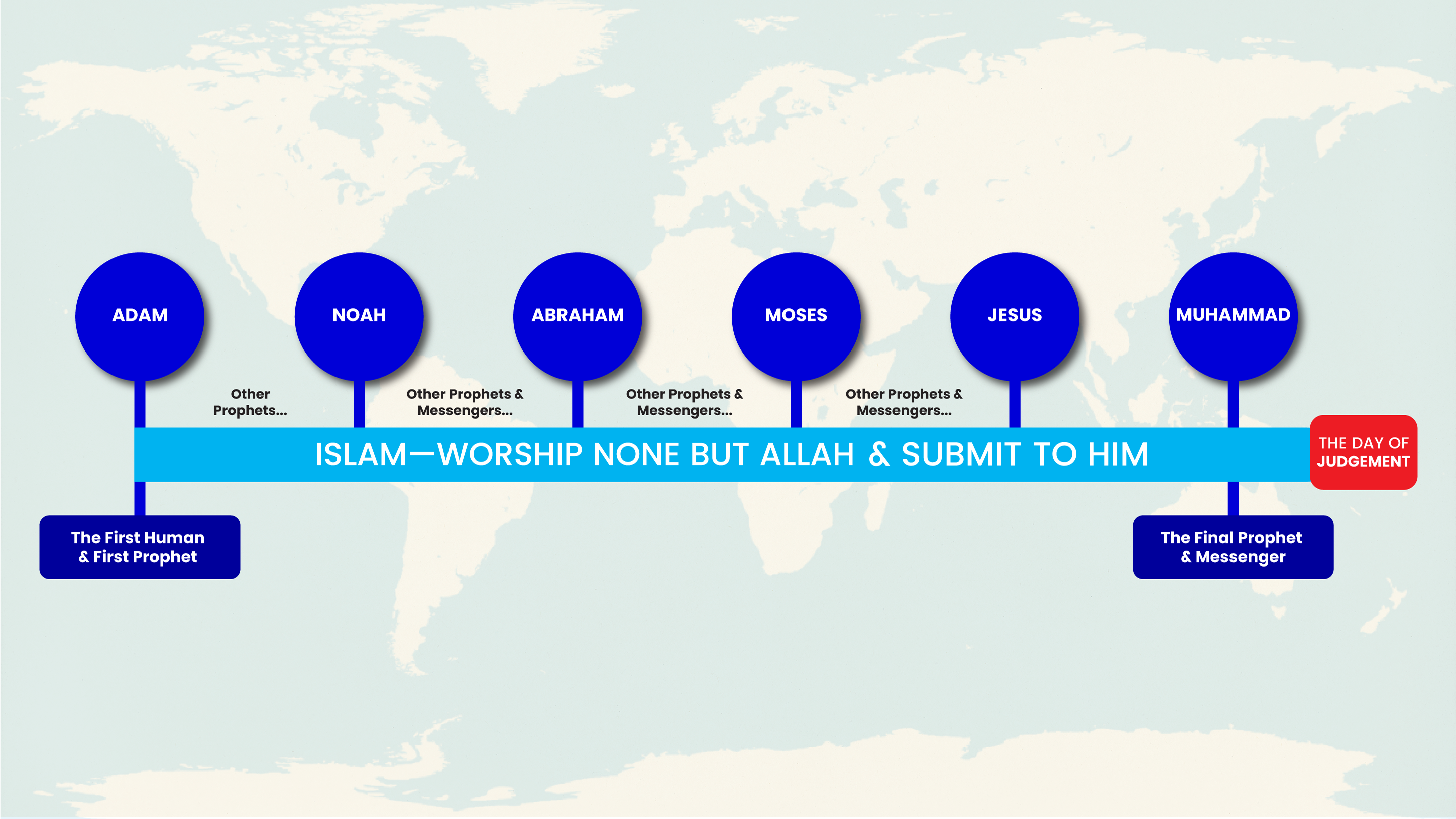
Prophets from Adam to Jesus
Prophethood is a divinelyordained institution through which Allah guided humanity throughout history. Allah, in His mercy and justice, did not leave any nation without guidance. He says: "And We certainly sent into every nation a messenger, [saying], 'Worship Allah and avoid false deities'" (Qur'an 16:36). This establishes that no people will be punished without first receiving clear proof and guidance.
The Unified Message - Tawheed:
From the first prophet Adam (peace be upon him) to the final prophet Muhammad ﷺ, the core message never changed: Worship Allah alone without any partners. While laws and specific legislations varied according to time, place, and need, the creed ('Aqeedah) of Tawheed remained constant and universal.
"And We sent not before you any messenger except that We revealed to him that, 'There is no deity except Me, so worship Me'" (Qur'an 21:25).
Key Prophets and Messengers:
Adam (peace be upon him) - The first human and first prophet. Allah created him with His hands, breathed into him from His Spirit, and taught him the names of all things. He was placed in Paradise but descended to earth after his mistake, where he repented and Allah forgave him. He taught his children Tawheed and worship.
Nuh/Noah (peace be upon him) - Called his people to Tawheed for 950 years with patience and wisdom. When they persisted in shirk and oppression, Allah saved him and the believers on the Ark and destroyed the disbelievers with the great flood. He is among the Ulul-'Azm (Messengers of firm resolve).
Ibrahim/Abraham (peace be upon him) - The Friend of Allah (Khalilullah) and father of the prophets. He was a champion of pure Tawheed who stood against his idolatrous people, including his own father. He broke their idols, debated them with clear proofs, and was thrown into a great fire by his people — but Allah commanded the fire to be cool and safe for him. He is the one who built the Ka'bah with his son Isma'il (Ishmael) and made the dua that led to the sending of Prophet Muhammad ﷺ. He is among the Ulul-'Azm prophets.
Isma'il/Ishmael (peace be upon him) - Son of Ibrahim, through whom the Arabs descended. He helped build the Ka'bah and was the one whom Ibrahim was commanded to sacrifice (according to the correct opinion of many scholars), showing complete submission to Allah.
Ishaq/Isaac (peace be upon him) - Son of Ibrahim, through whom the line of Israelite prophets came.
Ya'qub/Jacob (peace be upon him) - Also known as Isra'il, son of Isaac. The twelve tribes of Israel descended from his sons.
Yusuf/Joseph (peace be upon him) - Son of Ya'qub, who was thrown into a well by his brothers, sold into slavery in Egypt, falsely imprisoned, then elevated by Allah to become the treasurer of Egypt. His story in Surah Yusuf demonstrates patience, chastity, wisdom, and Allah's perfect plan.
Ayyub/Job (peace be upon him) - Tested severely with loss of wealth, children, and health, yet he remained patient and steadfast. A model of sabr (patience) in calamity.
Musa/Moses (peace be upon him) - One of the Ulul-'Azm prophets. Allah spoke to him directly (Kalimullah - the one to whom Allah spoke). He was sent to Fir'awn (Pharaoh) with clear signs and led the Children of Israel out of Egyptian slavery. He received the Tawrat (Torah) and established the divine law for his people. His story is the most frequently mentioned in the Qur'an, offering numerous lessons.
Harun/Aaron (peace be upon him) - Brother and assistant of Musa, who supported him in calling Fir'awn to Tawheed.
Dawud/David (peace be upon him) - Given the Zabur (Psalms), granted kingship and prophethood, praised Allah in beautiful recitation, and was given wisdom in judgment. He defeated Jalut (Goliath) as a youth through reliance on Allah.
Sulayman/Solomon (peace be upon him) - Son of Dawud, granted a magnificent kingdom, wisdom, and authority even over the jinn and wind. Despite his power, he remained humble and devoted to Allah. He is the one who said: "This is from the favor of my Lord to test me whether I will be grateful or ungrateful" (Qur'an 27:40).
Ilyas/Elijah (peace be upon him) - Called his people away from worshipping Baal and back to worshipping Allah alone.
Al-Yasa'/Elisha (peace be upon him) - Continued the mission after Ilyas.
Yunus/Jonah (peace be upon him) - Known as Dhun-Nun (The Man of the Fish). When he left his people in anger before Allah commanded him, he was swallowed by a whale. In the darkness of the whale's belly, he made the famous dua: "There is no deity except You; exalted are You. Indeed, I have been of the wrongdoers" (Qur'an 21:87). Allah responded to him and saved him.
Zakariyya/Zechariah (peace be upon him) - A righteous prophet who called upon Allah for a son in his old age, and Allah granted him Yahya.
Yahya/John (peace be upon him) - Son of Zakariyya, granted wisdom even as a youth, and commanded to hold firmly to the Scripture. He supported and testified to the truth of 'Isa (Jesus).
'Isa/Jesus (peace be upon him) - Son of Maryam (Mary), born miraculously without a father as a sign from Allah. He is one of the Ulul-'Azm prophets. He spoke as an infant in the cradle defending his mother's honor. He was given the Injil (Gospel) and performed many miracles by Allah's permission: healing the blind and leper, giving life to the dead, and creating a bird from clay (all by Allah's permission, not from his own power).
The Islamic Position on 'Isa (Jesus):
Important Principles About the Prophets:
1. They were human - Not divine or semi-divine. They ate, slept, married, had children, and died. Allah says about Muhammad ﷺ: "Say, 'I am only a man like you, to whom has been revealed that your god is one God'" (Qur'an 18:110).
2. They were chosen by Allah - Prophethood cannot be earned or achieved; it is Allah's choice. They were the best of their times in character, truthfulness, and trustworthiness.
3. They were protected from major sins ('Ismah) - Especially in conveying the message. They may have committed minor mistakes for which they immediately repented, teaching us how to seek forgiveness.
4. They were supported with miracles - As proof of their truthfulness (mu'jizat).
5. Their number - The exact number is not definitively established, but a hadith mentions 124,000 prophets and 315 messengers. We know the names of 25 mentioned explicitly in the Qur'an, and we believe in all of them.
6. We must believe in all of them - It is obligatory to believe in every prophet Allah sent. Rejecting even one prophet constitutes disbelief.
The Respect We Give Them:
Ahl al-Sunnah maintain the balanced middle path:
The legacy of these noble messengers teaches us that truth is one, guidance has always been available, and humanity has no excuse before Allah.
Stories of Major Prophets
The stories of the prophets in the Qur'an are not mere historical accounts or entertainment; they are divinely revealed narratives containing profound lessons, guidance, and reminders for all generations. Allah says: "Indeed in their stories, there is a lesson for men of understanding" (Qur'an 12:111).
The Story of Nuh (Noah) - Patience and Perseverance:
Prophet Nuh called his people to worship Allah alone for 950 years (Qur'an 29:14). Despite his tireless efforts using every approach — calling them publicly and privately, day and night — most refused and mocked him. They clung to their idols: Wadd, Suwa', Yaghuth, Ya'uq, and Nasr.
Key lessons from his story:
Allah says: "And We saved him and those with him in the ship, and We made it a sign for the worlds" (Qur'an 29:15). The story is found in detail in Surah Hud (11:25-49) and Surah Nuh (71).
The Story of Ibrahim (Abraham) - The Champion of Tawheed:
Ibrahim is called Khalilullah (the Friend of Allah) and Hanif (one inclined purely to truth). His story is the most frequently mentioned prophet's story after Musa.
Key aspects of his life:
The Story of Musa (Moses) - Law, Leadership, and Confronting Tyranny:
Musa's story is the most detailed in the Qur'an, mentioned in over 30 surahs. He is Kalimullah (the one to whom Allah spoke directly).
Key episodes:
The Story of 'Isa (Jesus) - The Messiah:
'Isa is among the greatest prophets and messengers, honored in Islam but not worshipped.
Islamic understanding:
Methodology of Ahl al-Sunnah:
Purpose of Messengers
Allah, in His perfect wisdom and mercy, sent messengers to guide humanity because human intellect alone cannot comprehend all aspects of worship, morality, and the Hereafter without divine guidance. The purposes of sending messengers are multiple and interconnected:
1. To Convey the Message of Tawheed:
The primary and central purpose is to call people to worship Allah alone without partners. Allah says: "And We sent not before you any messenger except that We revealed to him that, 'There is no deity except Me, so worship Me'" (Qur'an 21:25).
Every messenger came with this fundamental message: La ilaha illa Allah (None has the right to be worshipped except Allah). This establishes the foundation for all other guidance.
2. To Establish Proof Against Humanity:
Allah is the Most Just. He does not punish any people until He has sent them clear evidence through a messenger. Allah says: "And We never punish until We have sent a messenger" (Qur'an 17:15).
On the Day of Judgment, no one will be able to claim ignorance. The messengers came with clear signs (bayyinat) — miracles, scriptures, and rational arguments — that left no excuse for disbelief. This establishes Allah's absolute justice.
3. To Teach and Clarify:
Messengers explain to people:
Allah says about Prophet Muhammad ﷺ: "It is He who has sent among the unlettered a Messenger from themselves reciting to them His verses and purifying them and teaching them the Book and wisdom" (Qur'an 62:2).
4. To Give Glad Tidings and Warnings:
Messengers are mubashshireen (bearers of glad tidings) and mundhireen (warners). They:
This balanced approach motivates people through hope (raja') and fear (khawf), leading to proper worship based on love, hope, and awe of Allah.
5. To Serve as Role Models:
Messengers embody the teachings they convey. Their lives are practical demonstrations of how to implement divine guidance. Allah says about Prophet Muhammad ﷺ: "There has certainly been for you in the Messenger of Allah an excellent pattern" (Qur'an 33:21).
We learn:
6. To Judge Between People:
Messengers and the scriptures they brought serve as the criterion to resolve disputes. Allah says: "Mankind was [of] one religion [before their deviation]; then Allah sent the prophets as bringers of good tidings and warners and sent down with them the Scripture in truth to judge between the people concerning that in which they differed" (Qur'an 2:213).
Without divine revelation, people's opinions differ endlessly. The messengers bring objective truth from Allah.
7. To Purify Souls and Societies:
Messengers don't just convey information; they transform individuals and communities. They purify hearts from:
They cultivate:
Obedience to Messengers is Obedience to Allah:
Allah has made obedience to His messengers a part of obedience to Him. "He who obeys the Messenger has obeyed Allah" (Qur'an 4:80).
Following the messenger is not optional; it's essential to salvation. This is why rejecting even one messenger is kufr, and why innovations (bid'ah) in religion are rejected — because they contradict the messenger's perfect example.
The Finality:
With Prophet Muhammad ﷺ, the line of messengers was sealed. He was sent to all of humanity and jinn until the Day of Judgment. His message is universal and timeless. Allah says: "And We have not sent you except as a mercy to the worlds" (Qur'an 21:107).
The need for new prophets ended because:
Therefore, recognizing the purpose of messengers helps us appreciate why following the final messenger, Muhammad ﷺ, upon the understanding of the Salaf (the Companions and early generations), is the only path to salvation.
Previous Scriptures
Throughout history, Allah revealed divine scriptures to guide humanity through His chosen messengers. Belief in all the divinely revealed books is one of the six pillars of iman (faith). However, understanding the current state of these scriptures and how Muslims should interact with them requires careful clarification based on Qur'an and Sunnah.
The Major Revealed Scriptures:
1. The Suhuf (Scrolls) of Ibrahim and Musa: Earlier revelations mentioned in the Qur'an (87:18-19). Their exact content is unknown, and they are no longer extant.
2. The Tawrat (Torah): Revealed to Prophet Musa (Moses). It contained guidance and light for the Children of Israel. Allah says: "Indeed, We sent down the Torah, in which was guidance and light" (Qur'an 5:44).
3. The Zabur (Psalms): Given to Prophet Dawud (David). Allah says: "And We gave to David the Zabur" (Qur'an 4:163). These were praises and supplications.
4. The Injil (Gospel): Revealed to Prophet 'Isa (Jesus). It confirmed the Torah and provided additional guidance. Allah says: "And We sent, following in their footsteps, Jesus, the son of Mary, confirming that which came before him in the Torah; and We gave him the Gospel, in which was guidance and light" (Qur'an 5:46).
5. The Qur'an: The final and preserved revelation to Prophet Muhammad ﷺ, serving as the criterion (furqan) and guardian (muhaymin) over all previous scriptures.
The Issue of Alteration (Tahrif):
The Qur'an clearly states that the previous scriptures have been altered, corrupted, and mixed with human additions over time. This corruption took different forms:
Textual Alteration (Tahrif al-Lafz):
Allah says: "So woe to those who write the 'scripture' with their own hands, then say, 'This is from Allah,' in order to exchange it for a small price" (Qur'an 2:79).
Alteration of Meaning (Tahrif al-Ma'na):
Allah says: "Among the Jews are those who distort words from their [proper] usages and say, 'We hear and disobey'" (Qur'an 4:46).
Allah also says: "And indeed, there is among them a party who alter the Scripture with their tongues so you may think it is from the Scripture, but it is not from the Scripture. And they say, 'This is from Allah,' but it is not from Allah" (Qur'an 3:78).
Evidence of Corruption:
Historical and textual evidence confirms this:
The Muslim Position - The Balanced Approach:
Ahl al-Sunnah maintain a balanced and principled stance toward previous scriptures:
1. We believe in their original divine origin: It is obligatory to believe that Allah revealed the Torah, Zabur, and Injil. Denying this is kufr (disbelief). These were true revelations from Allah at the time they were revealed.
2. We affirm they have been corrupted: Based on clear Qur'anic evidence, we believe the current versions available (Bible, Torah) contain a mixture of:
3. We do not rely on them for legislation or creed: Since these books have been altered and are not preserved, we do not take rulings, beliefs, or practices from them. The Qur'an and authentic Sunnah are sufficient and authoritative.
4. We apply a three-part principle to their contents:
a) What the Qur'an confirms: We believe in it (e.g., the Oneness of Allah, prophethood, the Hereafter, basic moral principles).
b) What the Qur'an denies: We reject it (e.g., Trinity, Jesus being the son of God, original sin, contradictions to Islamic teachings).
c) What the Qur'an neither confirms nor denies: We neither believe nor disbelieve. We say, "We believe in what Allah revealed," and we don't rely on it. This includes specific historical details or stories not mentioned in our sources.
The Prophet Muhammad ﷺ said: "Do not believe the People of the Scripture, nor disbelieve them, but say: 'We believe in Allah and what has been revealed to us...'" (Sahih al-Bukhari).
5. We don't need to read them: There's no religious obligation or benefit for Muslims to study the Bible or Torah. The Qur'an and Sunnah contain all the guidance we need. Umar ibn al-Khattab (may Allah be pleased with him) once brought some writings from the Torah to the Prophet ﷺ, who became angry and said: "Are you in doubt, O son of Al-Khattab? ... If Musa were alive, he would have no option but to follow me" (Ahmad - Sahih).
The Qur'an as Muhaymin (Guardian/Criterion):
Allah describes the Qur'an as "muhaymin" over previous scriptures (Qur'an 5:48). This means:
Practical Implications:
This balanced understanding protects Muslims from confusion while maintaining respect for Allah's original revelations to previous prophets.
Need for Final Revelation
The sending of Prophet Muhammad ﷺ with the Qur'an as the final revelation was not arbitrary or coincidental; it was necessitated by divine wisdom and human need. Several interconnected reasons made a final, universal, and preserved message essential:
1. Corruption of Previous Scriptures:
As established earlier, the Torah, Injil, and other scriptures were altered, lost, or mixed with human interpretation. This left humanity without pure, reliable divine guidance. The texts available today contain:
Allah says: "And indeed, there is among them a party who alter the Scripture with their tongues so you may think it is from the Scripture, but it is not from the Scripture" (Qur'an 3:78).
Humanity needed a revelation that would be permanently preserved without any alteration — and that is the Qur'an.
2. Temporary and Limited Scope of Previous Messages:
Earlier prophets were sent to specific peoples and for specific times. For example:
The laws (Shari'ah) given to previous nations differed according to their circumstances. Some things were forbidden for them that are allowed for us, and vice versa.
Allah says: "For each [religious following] We have made a law and a method" (Qur'an 5:48).
With globalization and the interconnection of humanity, there was a need for a universal message that addresses all people, in all times, until the Day of Judgment.
3. The Universality of the Final Message:
Unlike previous prophets, Muhammad ﷺ was sent as a mercy to all the worlds — to all of humanity and jinn, Arabs and non-Arabs, in every land and every era.
Allah says: "And We have not sent you except comprehensively to mankind as a bringer of good tidings and a warner" (Qur'an 34:28).
And: "Say, [O Muhammad], 'O mankind, indeed I am the Messenger of Allah to you all'" (Qur'an 7:158).
The Prophet Muhammad ﷺ said: "Every prophet was sent to his nation only, but I have been sent to all mankind" (Sahih al-Bukhari & Muslim).
This universality necessitated a final message because:
4. Divine Promise of Preservation:
For a message to guide all future generations, it must be protected from any corruption or loss. Allah took upon Himself the preservation of the Qur'an:
"Indeed, it is We who sent down the Qur'an and indeed, We will be its guardian" (Qur'an 15:9).
This preservation occurred through multiple means:
No other religious text in human history has this level of preservation.
5. Completion and Perfection of Religion:
With the Qur'an and the Sunnah of Prophet Muhammad ﷺ, the religion was completed. Nothing is missing, and nothing needs to be added.
Allah says: "This day I have perfected for you your religion and completed My favor upon you and have approved for you Islam as religion" (Qur'an 5:3).
This verse was revealed shortly before the Prophet's ﷺ death. It means:
6. Response to Human Development:
By the 7th century CE, humanity had reached a level of intellectual, social, and civilizational maturity that prepared them to receive and preserve a final, comprehensive message. The conditions were ripe:
7. Testimony Against All Nations on the Day of Judgment:
The final message ensures that no nation or generation can claim they were not warned or guided. The Qur'an's preservation and global reach means every people will have access to the truth.
Allah says: "This Qur'an has been revealed to me that I may warn you thereby and whomever it reaches" (Qur'an 6:19).
On the Day of Judgment, Prophet Muhammad ﷺ and his followers will testify that the message was delivered to the nations.
8. Sealing of Prophethood:
Prophet Muhammad ﷺ is the Seal of the Prophets (Khatam al-Nabiyyin). Allah says: "Muhammad is not the father of [any] one of your men, but [he is] the Messenger of Allah and last of the prophets" (Qur'an 33:40).
This finality means:
The Prophet ﷺ said: "The likeness of me in comparison to the other prophets is that of a man who built a house and perfected it and beautified it, except for the place of one brick. The people walked around it admiring it and saying, 'Would that the place of this brick be filled!' I am that brick, and I am the seal of the prophets" (Sahih al-Bukhari & Muslim).
Conclusion:
The final revelation was not just an option but a divine necessity to:
Therefore, following Islam — the final message — is not merely one option among many religions; it is the only valid path to Allah after the coming of Prophet Muhammad ﷺ. Any religion or scripture not in accordance with Islam is either abrogated (if it was originally from Allah) or false (if it was invented by people).
Miracles as Proofs
Miracles (mu'jizat) are extraordinary events that occur at the hands of prophets as proof of their truthfulness and as signs from Allah to validate their message. These are not magic tricks or natural phenomena; they are supernatural acts that break the normal laws of nature by Allah's will and power, specifically to support His chosen messengers.
The Purpose of Miracles:
1. To prove prophethood: Miracles serve as credentials that distinguish true prophets from false claimants. They are Allah's seal of approval on His messengers.
2. To establish evidence (hujjah): They remove any excuse for disbelief. When people witness clear supernatural signs, the truth becomes undeniable. If they still reject, they do so out of arrogance, not ignorance.
3. To strengthen believers' faith: Witnessing or learning about miracles increases certainty (yaqeen) and solidifies iman.
4. To challenge the experts: Often, miracles came in forms that matched what a civilization excelled at, then surpassed it completely — making the challenge more profound.
Characteristics of Prophetic Miracles:
Miracles of Different Prophets:
Musa (Moses): The Egyptians excelled in sorcery and magic. Musa's miracles directly challenged and defeated them:
The magicians, who were experts in illusion, immediately recognized that Musa's miracles were real and from Allah. They prostrated and declared belief, even in the face of Fir'awn's threats.
'Isa (Jesus): In his time, medicine and healing were highly developed. His miracles challenged the physicians:
The Qur'an consistently emphasizes: "by permission of Allah" (bi-idhnillah), teaching that 'Isa himself had no independent power — he was a servant and prophet.
Muhammad ﷺ: The Arabs excelled in eloquence, poetry, and rhetoric. The greatest miracle given to him was the Qur'an — a linguistic and literary masterpiece that no human can replicate.
The Qur'an - The Eternal Miracle:
The Prophet ﷺ said: "There was no prophet among the prophets but he was given signs because of which people believed in him. What I have been given is the Divine Revelation which Allah has revealed to me. So I hope that my followers will be more than those of any other prophet on the Day of Resurrection" (Sahih al-Bukhari & Muslim).
Physical Miracles of Prophet Muhammad ﷺ:
In addition to the Qur'an, authentic hadith document numerous physical miracles:
1. Splitting of the Moon (Inshiqaq al-Qamar): The Quraysh demanded a sign, so the Prophet ﷺ made a gesture and the moon split into two parts — one over Mount Abu Qubays and the other over another mountain, with the mountain between them visible. This is recorded in Sahih hadith and mentioned in the Qur'an: "The Hour has drawn near, and the moon has split" (Qur'an 54:1).
2. Isra and Mi'raj (Night Journey and Ascension): The Prophet ﷺ was taken from Makkah to Jerusalem in one night, then ascended through the seven heavens, meeting previous prophets, witnessing Paradise and Hell, and receiving the command of five daily prayers directly from Allah. This physical and spiritual journey is confirmed in the Qur'an (17:1) and detailed in authentic hadith.
3. Water Flowing from His Fingers: On multiple occasions, water flowed abundantly from between the Prophet's ﷺ fingers, quenching the thirst of hundreds of companions and their animals when they had no water. Narrated in Sahih al-Bukhari and Muslim from multiple companions.
4. Multiplication of Food: Small amounts of food would be blessed and would feed large numbers of people until they were satisfied, with food remaining. For example, a few dates or a small bowl of food feeding hundreds of soldiers.
5. Healing:
6. Trees and Stones Testifying: Trees would move to greet him, stones would make salaam, and a tree trunk would cry when he stopped leaning on it while giving sermons (the incident of the weeping palm trunk).
7. Speaking Animals: A camel complained to him about mistreatment, and he understood and addressed the issue.
8. Prophecies: Numerous specific prophecies came true:
9. Physical Radiance: His face would shine with light, especially during revelation.
10. Protection from Enemies: Despite numerous assassination attempts, Allah protected him. He once stood among his enemies while they couldn't see him (Qur'an 36:9).
The Difference Between Miracles and Magic:
Miracles (Mu'jizat):
Magic (Sihr):
The Importance for Muslims Today:
Allah says: "And even if We had sent down to you [O Muhammad] a written scripture on a page and they touched it with their hands, the disbelievers would say, 'This is not but obvious magic'" (Qur'an 6:7).
This teaches us that those who reject out of arrogance will find excuses even in the face of clear miracles. Therefore, our faith should be built on understanding, knowledge, and reflection on the signs Allah has placed all around us.
The Final Messenger & Final Revelation
Seerah of Prophet Muhammad ﷺ
Prophet Muhammad ﷺ, the final messenger sent to humanity, was born in Makkah in the Year of the Elephant (571 CE) into the noble tribe of Quraysh. His lineage traces back to Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) عليه السلام through Ismail. Even before prophethood, he was known among his people as As-Sadiq (the Truthful) and Al-Amin (the Trustworthy) because of his impeccable character, honesty, and fairness.
He lived a life of purity: he never worshipped idols, never drank alcohol, and never engaged in immoral practices common in pre-Islamic Arabia (Jahiliyyah). He spent much time in reflection, often retreating to the cave of Hira to worship Allah alone.
At age 40, revelation came to him through the Angel Jibrīl with the first verses of the Qur’an: “Read in the name of your Lord who created...” (Qur’an 96:1). This marked the beginning of his 23-year mission.
He called his people to worship Allah alone, to abandon idols, to uphold justice, mercy, and righteousness. His early followers faced severe persecution, and after 13 years of hardship in Makkah, Allah commanded migration to Madinah. There, the Prophet ﷺ established the first Islamic society based on faith, justice, mutual support, and obedience to Allah.
In Madinah, Islam flourished. Treaties were made, communities were united, and righteous laws were revealed. The Prophet ﷺ exemplified perfect character — humility, bravery, patience, generosity, and compassion. After 23 years of prophethood, he completed his mission, delivering the final sermon in which he said:
“This day I have perfected your religion for you, completed My favor upon you, and have chosen for you Islam as your religion.” (Qur’an 5:3)
Shortly after, he ﷺ passed away at age 63, having conveyed the message fully and faithfully.
His Mission & Mercy
Allah describes the mission of the Prophet ﷺ clearly:
“We have not sent you except as a mercy to the worlds.” (Qur’an 21:107)
He was sent:
To call humanity to worship Allah alone without partners.
To perfect noble character, as he said: “I was sent to perfect good manners.” (Sahih al-Bukhari in Adab al-Mufrad)
To guide people to success in this world and the next.
To remove ignorance, superstition, and injustice.
His mercy was universal:
Mercy to the poor: he never turned a beggar away.
Mercy to orphans and widows.
Mercy to animals: he forbade cruelty and commanded kindness.
Mercy even to enemies: he forgave those who harmed him when he had power over them.
Mercy to the world: guiding them away from shirk and sin, toward Tawheed and salvation.
His companions described him as the kindest, most patient, and most truthful of people. He spoke gently, smiled often, forgave easily, and lived simply even when offered wealth.
His Sunnah is not just a set of religious laws — it is a model for moral excellence.
Prophetic Miracles
Prophet Muhammad ﷺ was granted many miracles from Allah, the greatest of which is the Qur’an. Other authentic miracles include:
1. Splitting of the Moon
When the Quraysh demanded a sign, he pointed to the moon and, by Allah’s permission, it split into two distinct halves. (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
2. Water Flowing From His Fingers
During a journey when water was scarce, water flowed from his fingers and the Companions made wudu and drank. (Sahih al-Bukhari)
3. Multiplication of Food
Small amounts of food would become abundant by his supplication, feeding large groups. (Sahih al-Bukhari, Muslim)
4. The Night Journey (Isra and Mi‘raj)
He was taken from Makkah to Jerusalem and ascended through the heavens, shown the realities of the unseen, and received the command for Salah. (Sahih Muslim)
5. Prophecies That Came True
He accurately foretold future events — battles, political shifts, spread of Islam, and signs of the Last Day — all of which occurred as he described.
His miracles, character, and the Qur’an together establish him as the true Messenger of Allah.
What is the Qur'an?
The Qur’an is the literal Word of Allah, revealed to Prophet Muhammad ﷺ over 23 years through the Angel Jibrīl. It is not created, not the speech of a human, and not poetry. It is divine revelation in perfect Arabic.
Allah says:
“Indeed, it is We who sent down the Qur’an, and We will guard it.” (Qur’an 15:9)
The Qur’an is:
A book of guidance
A cure for the heart
A light that leads to truth
A mercy for those who believe
A manual for life, death, and the hereafter
Unlike previous scriptures, it has remained unchanged — because Allah preserved it Himself.
Structure, Themes, and Style
The Qur’an consists of 114 chapters, revealed in both Makkah and Madinah. It contains guidance, stories, commands, parables, wisdom, and warnings.
Major Themes:
Style:
The Qur’an’s style is unique—neither poetry nor normal speech. It uses perfect language, rhythm, and meaning. Its structure moves with divine wisdom, addressing the mind, heart, and soul simultaneously.
The Arabs, known for mastery of Arabic, were never able to produce anything like it despite being challenged repeatedly by Allah.
Preservation of the Qur'an
One of Islam’s greatest miracles is that the Qur’an is completely preserved—letter for letter—exactly as Allah revealed it.
Forms of Preservation:
1. Memorization: Millions have memorized the Qur’an entirely. This tradition began with the Prophet’s companions and continues unchanged today. 2. Written Compilation:
3. No Variations: Muslims across the world recite the same Qur’an. Authentic Qira’at are not versions but recitation modes taught by the Prophet ﷺ. 4. Global Transmission: Because it was memorized and written widely, no one could alter it—and no one ever has.
Allah fulfilled His promise: *“We will guard it.”* (15:9)
Miracles of the Qur'an
The Qur’an contains multiple layers of miracles that prove its divine origin:
1. Linguistic Miracle
Its Arabic structure, precision, and eloquence are unmatched. Allah challenged humanity: *“Produce a chapter like it.”* (Qur’an 2:23) None ever has.
2. Scientific Accuracy
It describes natural facts unknown at the time:
3. Historical Accuracy
It corrects distortions found in earlier scriptures and narrates events with perfect clarity.
4. Prophecies
The Qur’an accurately predicted events such as:
5. Transformative Power
It changes hearts, societies, and nations. Anyone who sincerely reflects on its verses finds guidance and peace.
The Qur’an’s miracles cannot be replicated or explained by human ability—it is divine.
Understanding Sunnah Correctly
The Sunnah is the second source of Islam after the Qur’an. It includes the sayings, actions, approvals, and lifestyle of the Prophet ﷺ. Allah commands:
*“Whoever obeys the Messenger has obeyed Allah.”* (Qur’an 4:80)
The Sunnah clarifies and completes the Qur’an:
Following Sunnah Correctly Means:
The Prophet ﷺ said: *“Whoever introduces into this matter of ours what is not from it, it will be rejected.”* (Sahih al-Bukhari & Muslim)
The Sunnah is not optional—it is essential. It is the practical application of the Qur’an and the way to follow the Messenger ﷺ with love, sincerity, and obedience.
Conclusion
The story of the Final Messenger and the Final Revelation is the story of Islam itself: a message of truth, mercy, and guidance sent for all humanity. The Prophet Muhammad ﷺ lived this message perfectly, and the Qur’an preserved it eternally.
Understanding the seerah, the Qur’an, its themes, its miracles, and the Sunnah forms the foundation for any sincere seeker of truth who wants to understand Islam as it truly is — pure, unchanged, and deeply life-changing.
The Deen – Islam, Iman, Ihsan

Islam: The 5 Pillars
Islam is the foundation of submission to Allah — outward actions that manifest faith. It represents the practical implementation of belief through specific acts of worship that Allah has commanded.
The Prophet ﷺ said: "Islam is built upon five: to testify that none has the right to be worshipped but Allah and that Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah, to establish the prayer, to give zakah, to fast Ramadan, and to perform Hajj." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
1. Shahada (Testimony of Faith)
The entrance to Islam, testifying: "La ilaha illa Allah, Muhammad Rasulullah" (None has the right to be worshipped except Allah, and Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah).
This testimony requires:
The first part affirms Tawheed al-Uluhiyyah (Allah alone deserves worship). The second part requires following the Prophet ﷺ upon the understanding of the Salaf, as innovation in religion is rejected.
2. Salah (Prayer)
The link between the servant and his Lord, establishing connection with Allah five times daily. The Prophet ﷺ said: "The first matter that the servant will be accountable for on the Day of Judgment is the prayer. If it is good, then the rest of his deeds will be good. And if it is bad, then the rest of his deeds will be bad." (Tabarani — Sahih)
The Five Daily Prayers:
Requirements:
Importance: Salah is the pillar of the religion. Whoever establishes it has established the religion, and whoever abandons it has destroyed the religion. The Prophet ﷺ said: "Between a man and shirk and kufr is the abandonment of prayer." (Sahih Muslim)
Prayer must be performed with khushu' (humility, focus, and presence of heart), understanding what is recited, and following the Sunnah in every detail.
3. Zakah (Obligatory Charity)
A purification of wealth and soul, obligatory upon those who possess nisab (minimum threshold of wealth). Allah says: "Take from their wealth a charity to purify them and sanctify them with it." (Qur'an 9:103)
Wisdom Behind Zakah:
Nisab and Amount:
Zakah is Not Optional: Withholding zakah is a major sin. The Prophet ﷺ warned that on the Day of Judgment, wealth that was not given in zakah will be made into a heated metal and used to brand the forehead, side, and back of the one who withheld it. (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
4. Sawm (Fasting in Ramadan)
Abstaining from food, drink, and marital relations from dawn (Fajr) until sunset (Maghrib) during the month of Ramadan. Allah says: "O you who have believed, decreed upon you is fasting as it was decreed upon those before you that you may become righteous." (Qur'an 2:183)
Purpose of Fasting:
Requirements:
The Prophet ﷺ said: "Whoever does not give up false speech and acting upon it, Allah has no need for him to give up his food and drink." (Sahih al-Bukhari)
Ramadan — The Blessed Month:
5. Hajj (Pilgrimage to Makkah)
A once-in-a-lifetime duty for those who are physically and financially able. Allah says: "And [due] to Allah from the people is a pilgrimage to the House - for whoever is able to find thereto a way." (Qur'an 3:97)
Hajj includes:
Virtues: The Prophet ﷺ said: "Whoever performs Hajj for Allah's sake, and does not commit any obscenity or sins, will return as the day his mother gave birth to him." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
He also said: "An accepted Hajj has no reward except Paradise." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
The Pillars Are Connected: These five pillars work together to shape a complete Muslim: the Shahada establishes belief; Salah maintains daily connection; Zakah purifies wealth; Sawm trains the soul; and Hajj unites the Ummah in worship at the House of Allah. Each pillar reinforces the others, and together they form the framework of a life devoted to Allah.
Iman: The 6 Articles of Faith
Iman resides in the heart, is expressed by the tongue, and acted upon by the limbs. It increases with obedience and decreases with sin. This is the belief of Ahl al-Sunnah wal-Jama'ah, supported by numerous texts from the Qur'an and Sunnah.
The Prophet ﷺ said: "To believe in Allah, His angels, His Books, His Messengers, the Last Day, and to believe in divine decree (Qadar), its good and its bad." (Hadith of Jibril – Sahih Muslim)
1. Belief in Allah
This is the foundation of faith and consists of three categories:
Tawheed al-Rububiyyah (Lordship): Affirming that Allah alone is the Creator, Sustainer, Provider, and Controller of all affairs. No one shares with Him in His dominion. Allah says: "Indeed, your Lord is Allah, who created the heavens and earth in six days and then established Himself above the Throne. He covers the night with the day, [another night] chasing it rapidly; and [He created] the sun, the moon, and the stars, subjected by His command. Unquestionably, His is the creation and the command; blessed is Allah, Lord of the worlds." (Qur'an 7:54)
Tawheed al-Uluhiyyah (Worship): Singling out Allah alone for all forms of worship — no worship is directed to anyone or anything else. This includes du'a (supplication), fear, hope, love, trust, sacrifice, vows, and seeking help. Allah says: "And your Lord says, 'Call upon Me; I will respond to you. Indeed, those who disdain My worship will enter Hell [rendered] contemptible.'" (Qur'an 40:60)
Tawheed al-Asma' was-Sifat (Names and Attributes): Affirming for Allah all the beautiful Names and perfect Attributes that He affirmed for Himself or that His Messenger ﷺ affirmed for Him, in a manner that suits His Majesty — without distortion, denial, asking "how," or likening Him to creation. Allah says: "There is nothing like unto Him, and He is the All-Hearer, the All-Seer." (Qur'an 42:11)
2. Belief in the Angels
Angels are created from light, noble beings who worship Allah day and night without tiring. They do not disobey Allah and do whatever they are commanded. Allah says: "To Allah prostrates whoever is within the heavens and the earth, willingly or by compulsion, and their shadows [as well] in the mornings and the afternoons." (Qur'an 13:15)
Notable Angels:
Why We Believe in Them: Belief in angels is essential because they carry out Allah's commands in this universe. Denying their existence is disbelief. Allah says: "Whoever disbelieves in Allah, His angels, His books, His messengers, and the Last Day has certainly gone far astray." (Qur'an 4:136)
3. Belief in the Books
Allah revealed scriptures to guide humanity. We believe in all of them, but follow only the Qur'an, as it abrogates previous scriptures.
The Major Revealed Books:
The Qur'an: The final revelation, unchanged and preserved by Allah Himself. Allah says: "Indeed, it is We who sent down the Qur'an and indeed, We will be its guardian." (Qur'an 15:9)
It is the ultimate source of guidance. The Prophet ﷺ said: "I have left among you that which if you hold fast to it, you will never go astray: the Book of Allah." (Sahih Muslim)
4. Belief in the Messengers
Allah sent messengers to every nation to call them to Tawheed and warn them against shirk (associating partners with Allah). Allah says: "And We certainly sent into every nation a messenger, [saying], 'Worship Allah and avoid false deities.'" (Qur'an 16:36)
We must believe:
The Prophet ﷺ said: "The similitude of mine and that of the prophets before me is that of a man who built a house excellently and beautifully, except for the place of one brick. People went around it and wondered at it, saying: 'If only this brick were put in its place!' So I am that brick, and I am the seal of the prophets." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
5. Belief in the Last Day
The Day of Judgment is a reality that will come. This includes belief in:
Death and the Barzakh (Life in the Grave): After death, the soul enters an intermediate realm. The grave will be either a garden from the gardens of Paradise or a pit from the pits of Hell. Munkar and Nakir will question the deceased about their Lord, religion, and Prophet.
The Resurrection: Allah will resurrect all people from their graves. Allah says: "And the Horn will be blown; and at once from the graves to their Lord they will hasten." (Qur'an 36:51)
The Gathering and Reckoning: All will stand before Allah. Their deeds will be weighed, and they will be held accountable. Allah says: "And We place the scales of justice for the Day of Resurrection, so no soul will be treated unjustly at all." (Qur'an 21:47)
The Bridge (As-Sirat): A bridge over Hell that everyone must cross. The believers will pass according to their deeds, while the disbelievers will fall into the Fire.
Paradise and Hell: Eternal destinations. Paradise is the abode of the believers, filled with unimaginable delights. Hell is the abode of the disbelievers, filled with punishment. Allah says: "Indeed, the righteous will be in gardens and rivers, in a seat of honor near a Sovereign, Perfect in Ability." (Qur'an 54:54-55)
6. Belief in Qadar (Divine Decree)
Belief in Qadar has four levels:
1. Knowledge: Allah knows everything that has happened and will happen. Nothing escapes His knowledge. Allah says: "Indeed, Allah is Knowing of all things." (Qur'an 2:231)
2. Writing: Allah has written all that will occur until the Day of Judgment in Al-Lawh al-Mahfuz (the Preserved Tablet). The Prophet ﷺ said: "Allah wrote the decrees of creation fifty thousand years before He created the heavens and the earth." (Sahih Muslim)
3. Will: Nothing occurs except by Allah's will. Whatever Allah wills happens, and whatever He does not will does not happen. Allah says: "And you do not will except that Allah wills." (Qur'an 76:30)
4. Creation: Allah is the Creator of all things, including the actions of His servants. Allah says: "Allah is the Creator of all things, and He is, over all things, Disposer of affairs." (Qur'an 39:62)
However: Humans have free will and are responsible for their choices. They are not forced to sin. Allah has given them ability, choice, and guidance. The one who obeys does so by his choice, and the one who disobeys does so by his choice — but all within the framework of Allah's will and decree.
The Balance: Ahl al-Sunnah affirm both divine decree and human responsibility. We do not use Qadar as an excuse for sin. The Prophet ﷺ said: "Work, for everyone is facilitated to that for which he was created." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
Why These Six? These pillars of faith encompass belief in the unseen. They shape our worldview: we recognize Allah as our Creator and sole object of worship; we acknowledge His perfect execution of His will through angels; we follow His guidance through His Books and Messengers; we prepare for the Hereafter; and we trust His wisdom in all that He decrees. Together, they anchor the believer in certainty, purpose, and submission.
Ihsan: Worship with Excellence
Ihsan is the highest level of the Deen, representing perfection in worship and behavior. It is to worship Allah as though you see Him, and while you do not see Him, He surely sees you.
The Prophet ﷺ said: "Ihsan is to worship Allah as if you see Him; if you cannot see Him, know that He sees you." (Hadith of Jibril – Sahih Muslim)
The Meaning of Ihsan
Linguistically: Ihsan means excellence, perfection, and beauty.
Islamically: It means performing acts of worship with complete sincerity, humility, focus, and perfection — as if you are in the direct presence of Allah, seeing Him before you. And if you cannot reach that level of consciousness, then at least knowing with certainty that Allah sees you, watches you, and is aware of every movement, thought, and intention.
The Two Levels of Ihsan
First Level: "As if you see Him" This is the higher level. The worshipper is so immersed in awareness of Allah's majesty that it is as though he sees Allah before him. His heart is filled with awe, love, hope, and fear. This level is rare and represents the station of the closest servants of Allah.
Second Level: "He sees you" This is more attainable. The worshipper realizes that even though he does not see Allah, Allah sees him completely — every action, word, and hidden thought. This awareness leads to guarding one's worship, purifying intentions, and avoiding sin. Allah says: "Does he not know that Allah sees?" (Qur'an 96:14)
Ihsan in Worship
Ihsan transforms routine rituals into acts of profound devotion:
In Salah: Praying with focus and khushu', contemplating the meanings of what is recited, feeling the greatness of standing before Allah, and perfecting every posture and movement.
In Fasting: Not merely abstaining from food and drink, but guarding the tongue, eyes, and heart from sin, knowing Allah sees even what is hidden.
In Zakah: Giving with sincerity, choosing the best of one's wealth, not seeking praise from people, and giving for Allah's sake alone.
In Hajj: Performing every rite correctly, with devotion and humility, as an act of pure submission.
In All Actions: Doing everything for Allah's sake, perfecting one's manners, fulfilling trusts, and treating people with kindness and justice — all while conscious of Allah's watchfulness.
Ihsan Requires Ikhlas (Sincerity)
The essence of Ihsan is ikhlas — sincerity in worship for Allah alone, free from showing off or seeking worldly gain. Allah says: "And they were not commanded except to worship Allah, [being] sincere to Him in religion." (Qur'an 98:5)
The Prophet ﷺ said: "Indeed, Allah does not look at your forms or your wealth, but He looks at your hearts and your deeds." (Sahih Muslim)
Without ikhlas, worship is empty form. With it, even small deeds become weighty. Ihsan is the actualization of ikhlas in every action.
Ihsan Cultivates Muraqabah (Vigilance)
Muraqabah is the continuous awareness that Allah is watching. This consciousness guards against sin in private, motivates good deeds, and keeps the heart attached to Allah at all times.
The Prophet ﷺ said: "Have haya (modesty/shame) before Allah as He truly deserves." The Companions asked, "How?" He replied: "Whoever guards the head and what it contains, and the stomach and what it contains, and remembers death and the trial, then he has had haya before Allah as He deserves." (Tirmidhi — Hasan)
Ihsan in Behavior
Ihsan extends beyond worship to all of life:
With Family: Treating them with kindness, patience, and mercy.
With Neighbors and Community: Being helpful, avoiding harm, and spreading goodness.
With All of Creation: The Prophet ﷺ said: "Indeed, Allah has prescribed Ihsan in everything. So if you kill, kill well; and if you slaughter, slaughter well. Let one of you sharpen his blade and give ease to his animal." (Sahih Muslim)
Even in how we treat animals, Ihsan is required. How much more so in how we deal with fellow human beings?
How to Develop Ihsan
The Fruit of Ihsan
Those who worship with Ihsan attain:
Allah says: "Is the reward for Ihsan anything but Ihsan?" (Qur'an 55:60) — Meaning, the one who perfects his worship will be rewarded with the perfection of Paradise.
Conclusion: Ihsan is the soul of Islam. Without it, worship becomes mechanical. With it, every moment is alive with purpose, every action carries weight, and the heart finds peace in the remembrance of Allah. Ihsan is not just a state for the elite; it is a goal every Muslim must strive toward by making worship and behavior as perfect as possible, as if standing before Allah — because indeed, He sees.
The Relationship Between the Three
Islam, Iman, and Ihsan are not three separate religions, but three dimensions of one comprehensive Deen. Understanding their relationship is essential to developing a complete Islamic personality.
Three Levels, One Deen
The Hadith of Jibril (Sahih Muslim) teaches us that Islam, Iman, and Ihsan are interconnected levels of the religion:
Islam — The foundation: outward acts of submission. Iman — The core: inward belief and conviction. Ihsan — The pinnacle: perfection in worship and consciousness of Allah.
Together, they form a holistic system that encompasses belief, action, and spiritual excellence.
Islam: The Body
Islam consists of the Five Pillars — the visible, outward actions that define a Muslim's submission to Allah. These are the first and most basic requirements:
Without Islam, there is no entry into the religion. It is the minimum required. A person can be a Muslim by performing these pillars, even if his Iman is weak.
Iman: The Heart
Iman is belief in the Six Articles of Faith — matters of the unseen that reside in the heart and are affirmed by the tongue. Iman is deeper than Islam; it involves conviction, understanding, and internal acceptance.
Iman consists of:
Ahl al-Sunnah wal-Jama'ah affirm that actions are part of faith. Faith increases with obedience and decreases with disobedience. Allah says: "The believers are only those who, when Allah is mentioned, their hearts become fearful, and when His verses are recited to them, it increases them in faith." (Qur'an 8:2)
This contrasts with deviant groups who claim faith is only in the heart and does not increase or decrease. Ahl al-Sunnah follow the Qur'an, Sunnah, and understanding of the Salaf: Faith = belief + speech + action, and it increases and decreases.
Ihsan: The Soul
Ihsan is the perfection of both Islam and Iman. It is the state of worshipping Allah with complete awareness, sincerity, and excellence — "as if you see Him."
Ihsan transforms rituals from routine to devotion, from habit to heartfelt worship. A person may pray (Islam) and believe in Allah (Iman), but does he pray with full focus and humility (Ihsan)? Ihsan is what brings life to worship.
How They Work Together
Think of Islam, Iman, and Ihsan as three concentric circles:
1. The Outer Circle (Islam): All who perform the pillars. This includes those with weak or strong Iman.
2. The Middle Circle (Iman): Those who not only practice Islam but have deep conviction and understanding of the articles of faith.
3. The Inner Circle (Ihsan): Those who worship with perfection, consciousness, and sincerity.
Everyone in the inner circle has the middle and outer circles; everyone in the middle circle has the outer circle. But not everyone in the outer circle has achieved the inner circles.
Can You Have One Without the Other?
Islam Without Iman: A person may outwardly perform the pillars (Islam) while inwardly lacking true belief (Iman). This is the state of hypocrites (munafiqun). Their Islam is outward appearance only; their hearts are devoid of faith. Such a person is not truly Muslim in Allah's sight.
Iman Without Islam: This is impossible. True Iman requires action. If someone claims to believe but refuses to pray, pay Zakah, or fulfill the pillars, his claim of Iman is false. As Ahl al-Sunnah affirm: faith includes action. A person who intentionally abandons Salah, for example, has left Islam, according to the majority view, based on the Prophet's ﷺ statement: "Between a man and shirk and kufr is the abandonment of prayer." (Sahih Muslim)
Islam and Iman Without Ihsan: A person may have Islam and Iman but lack Ihsan. He prays, but without focus. He fasts, but continues to backbite. He gives Zakah, but for show. Such a person is a believer, but his faith is incomplete, and his reward is less.
The Goal: All Three The complete Muslim is one who embodies Islam (actions), Iman (belief), and Ihsan (excellence). This is the person described in the Qur'an as having attained taqwa (consciousness of Allah).
The Prophetic Model
The Prophet Muhammad ﷺ exemplified all three perfectly:
He ﷺ is the model every Muslim must strive to follow. Allah says: "There has certainly been for you in the Messenger of Allah an excellent pattern for anyone whose hope is in Allah and the Last Day and [who] remembers Allah often." (Qur'an 33:21)
The Path Forward
To develop a complete Islamic personality:
1. Establish Islam: Fulfill the Five Pillars with consistency and correctness. 2. Strengthen Iman: Study the Six Articles of Faith, increase knowledge of Allah, His names and attributes, and fortify your heart with certainty. 3. Cultivate Ihsan: Worship with presence of heart, purify your intentions, and live with constant awareness of Allah's watchfulness.
This is the path of the Prophets, the Companions, and the righteous Salaf. May Allah grant us the ability to embody Islam, Iman, and Ihsan in their completeness.
Balance of Ritual and Spirituality
True Islam unites body and soul, outward action and inward intention, visible worship and hidden devotion. There is no Islam without law, and no spirituality without following the Sunnah.
The Islamic Approach: Integration, Not Separation
Some religions emphasize rituals without spirituality, becoming dry formalism. Others emphasize spirituality without law, leading to innovation and deviation. Islam balances both:
Rituals (Actions): Obligatory acts like Salah, fasting, Zakah, and Hajj — clear, defined, and unchangeable.
Spirituality (Heart): Sincerity, humility, love of Allah, fear, hope, trust, and consciousness — the inner dimension.
Neither is valid without the other. The Prophet ﷺ said: "Indeed, Allah does not look at your forms or your wealth, but He looks at your hearts and your deeds." (Sahih Muslim)
Your deeds must be correct (following the Sunnah), and your heart must be pure (free from showing off and insincerity).
Worship Without Heart: Empty Ritual
Performing Salah without focus, fasting without controlling the tongue, or giving charity for show — these are actions lacking the soul of worship. The body moves, but the heart is absent.
Allah says: "Indeed, prayer prohibits immorality and wrongdoing." (Qur'an 29:45) If Salah does not impact behavior, it has not been performed with its intended spirit.
The Prophet ﷺ said: "Whoever does not abandon false speech and acting upon it, Allah has no need for him to give up his food and drink." (Sahih al-Bukhari) — Fasting must purify the soul, not just the stomach.
The Danger: Worship becomes routine, habits without meaning. The Muslim becomes heedless, his heart hardened, his worship mechanical. This is the state of many today — outward religiosity, inward emptiness.
Spirituality Without Law: Misguided Innovation
Some claim to have "spiritual connection" while abandoning or altering Salah, or introducing acts of worship not taught by the Prophet ﷺ. This is deviation.
True spirituality is achieved only through following the Sunnah, not by inventing new forms of worship. The Prophet ﷺ said: "Whoever introduces into this affair of ours what is not from it, it is rejected." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
Sufi orders that engage in innovations — such as dhikr in circles, loud chanting not from the Sunnah, or seeking intermediaries besides Allah — have deviated from the path of the Salaf. True spirituality is in the Sunnah, not in bid'ah (innovation).
Allah says: "Say, [O Muhammad], 'If you love Allah, then follow me, [so] Allah will love you and forgive you your sins.'" (Qur'an 3:31)
The Danger: Following desires instead of revelation. Spirituality becomes based on feelings, culture, or innovation — not on the Qur'an and Sunnah. This leads to misguidance and may reach shirk (associating partners with Allah).
The Prophetic Balance
The Prophet ﷺ combined both dimensions perfectly:
He prayed with devotion: Standing so long that his feet would swell. When asked why he exerted himself so much when Allah had forgiven his sins, he replied: "Should I not be a grateful servant?" (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
He wept in Salah: His Companions could hear him weeping as he recited the Qur'an in prayer. His heart was alive with love and fear of Allah.
He perfected the outward: He taught his Companions the precise way to make wudu, pray, fast, and perform every act of worship.
He purified the inward: He constantly supplicated: "O Allah, I seek refuge in You from knowledge that does not benefit, a heart that does not fear, a soul that is not satisfied, and a supplication that is not answered." (Sahih Muslim)
He was the living embodiment of Islam, Iman, and Ihsan — actions, beliefs, and excellence united.
How to Achieve Balance
1. Learn the correct way of worship: Study the Sunnah. Know how the Prophet ﷺ prayed, fasted, and worshipped. Follow it exactly. Innovation has no place in worship.
2. Purify the intention: Before every act of worship, check your niyyah (intention). Are you doing it for Allah alone, or for people to see? The Prophet ﷺ said: "Actions are judged by intentions." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
3. Develop khushu' (humility and focus): In Salah, contemplate the meanings of what you recite. Feel that you are standing before Allah. Remove distractions. Make du'a from the heart.
4. Seek knowledge: Increase your understanding of Allah's names, attributes, and His greatness. The more you know Allah, the more your heart will be filled with awe, love, and fear.
5. Be consistent: The Prophet ﷺ said: "The most beloved of deeds to Allah are those that are consistent, even if small." (Sahih al-Bukhari, Sahih Muslim)
6. Avoid extremes: Do not exaggerate in worship beyond the Sunnah, and do not be negligent. The Prophet ﷺ warned against ghuluw (exaggeration) in religion. He said: "Beware of extremism in religion, for those before you were destroyed due to extremism in religion." (Nasa'i, Ibn Majah — Sahih)
7. Constantly make du'a for guidance: Ask Allah to grant you sincerity, Ihsan, and steadfastness. The heart is between the two fingers of the Most Merciful; He turns it as He wills.
The Fruit of Balance
When a Muslim combines correct action with sincere intention, he attains:
Allah says: "Those who have believed and whose hearts are assured by the remembrance of Allah. Unquestionably, by the remembrance of Allah hearts are assured." (Qur'an 13:28)
Conclusion: True spirituality in Islam is not abandoning the law or creating new rituals. It is following the Sunnah with a sincere heart, perfecting the outward while purifying the inward, and combining the body's submission with the soul's devotion. This is the path of the Prophet ﷺ and the Salaf — may Allah grant us the ability to follow it.
Sunnah and Bid'ah
The Sunnah represents the Prophet’s authentic teachings and the path of his companions. The Salaf warned that innovation leads to misguidance. “The best speech is the Book of Allah, and the best guidance is the guidance of Muhammad ﷺ. The worst of affairs are newly invented matters.” (Sahih Muslim)
Ahl al-Sunnah adhere to Qur'an and Sunnah upon the understanding of the Companions, avoiding excess and neglect, and preserving the purity of Islam.
Islamic Lifestyle: Morality, Family, and Society
Ethics and Morality
Islamic morality is rooted in Tawheed, sincerity to Allah, and following the character of the Prophet ﷺ. He said: “I was only sent to perfect righteous character.” (Musnad Ahmad – Sahih)
A Muslim’s ethics are not cultural or subjective — they come from divine revelation.
Core Moral Qualities in Islam
“Do not let the hatred of a people cause you to be unjust. Be just; that is nearer to righteousness.” (Qur’an 5:8)
Enjoining Good and Forbidding Evil
This is a defining quality of the Muslim Ummah. Allah says: “You are the best nation raised for mankind: you enjoin what is right and forbid what is wrong.” (Qur’an 3:110)
This duty is carried out with wisdom, patience, and gentleness — following the prophetic method.
Family Life
Family is the foundation of a healthy Islamic society. Marriage, parenting, and kinship are acts of worship and responsibilities entrusted by Allah.
Marriage
Allah describes marriage as a sign of His mercy: “He created for you spouses that you may find tranquility in them, and He placed between you affection and mercy.” (Qur’an 30:21)
Marriage in Islam is built on:
Parents
Righteous treatment of parents comes immediately after worshipping Allah. “Your Lord has decreed that you worship none but Him, and that you show kindness to parents.” (Qur’an 17:23)
Obedience, gratitude, and gentle speech toward parents are emphasized throughout the Qur’an and Sunnah.
Children
Children are a trust (amanah). Parents must:
The Prophet ﷺ said: “A father gives his child nothing better than good character.” (Tirmidhi – Hasan)
Kinship (Silat ar-Rahim)
Maintaining family ties brings blessings, increases provision, and extends lifespan. The Prophet ﷺ said: “Whoever wishes for his provision to be increased and his lifespan extended, let him maintain ties of kinship.” (Sahih al-Bukhari)
Family harmony is a sign of faith and obedience to Allah.
Social Conduct
Islam teaches a way of life that builds a compassionate, fair, and safe society. The believer is beneficial everywhere he goes.
Business and Financial Ethics
Islamic law prohibits:
Honesty in trade is a mark of righteousness. The Prophet ﷺ said the honest merchant will be with the prophets, truthful ones, and martyrs (Tirmidhi – Hasan).
Neighbors
Islam places special emphasis on neighbors. The Prophet ﷺ said: “He is not a believer whose neighbor is not safe from his harm.” (Sahih al-Bukhari)
Kindness to neighbors applies regardless of their religion or background.
Community Responsibility
Allah commands: “Cooperate in righteousness and piety, but do not cooperate in sin and transgression.” (Qur’an 5:2)
A Muslim strives to:
This creates a society rooted in mercy and guided by divine principles.
Seeking Knowledge
Knowledge is the foundation of correct belief and worship. The Prophet ﷺ said: “Seeking knowledge is an obligation upon every Muslim.” (Ibn Majah – Sahih)
Why Knowledge Matters
What to Learn First
A new Muslim should begin with:
From Whom to Learn
Knowledge must be taken from:
This ensures that a Muslim avoids innovations, extremism, and incorrect beliefs.
Seeking knowledge with sincerity is a lifelong journey that brings light to the heart and guidance to life.
The Hereafter

What Happens After Death
The moment the soul leaves the body, a human enters al-Barzakh, the life between this world and the Day of Resurrection. The Prophet ﷺ said: “The grave is either a garden from the gardens of Paradise or a pit from the pits of Hell.” (Tirmidhi, Sahih)
When a believer dies, angels with radiant faces come to take his soul gently, bringing fragrance and glad tidings. The disbeliever or hypocrite is met by harsh angels who pull the soul painfully.
Questioning in the Grave
Two angels — Munkar and Nakir — ask three essential questions:
The believer answers with firmness because of his faith and good deeds. The disbeliever and hypocrite falter and say, “I don’t know.”
After this, the soul’s state begins:
This stage continues until the final resurrection.
Day of Resurrection
The Day of Resurrection (Yawm al-Qiyamah) begins when Allah orders the Trumpet to be blown. All creation dies, and with a second blowing, all are resurrected from their graves for the final judgment.
Allah says: “As He began the first creation, so He will repeat it.” (Qur’an 21:104)
Humanity will stand barefoot, uncircumcised, and uncLOthed, overwhelmed by fear as the sun draws near. Every soul will be concerned only for its own outcome.
Records & Scales
Every person’s deeds will be presented openly.
The Prophet’s Pond (Hawd)
The Prophet ﷺ will have a vast pond. Whoever drinks from it will never thirst again.
Intercession
The greatest intercession (Shafa‘ah al-‘Uzma) belongs only to the Prophet Muhammad ﷺ — by Allah’s permission. He will intercede for the beginning of judgment and for believers who committed sins. All intercession belongs to Allah alone and is given only to those He is pleased with.
Accountability and the Scales
On that Day, perfect justice will be established. No oppression, no favoritism, no hidden actions — everything is known to Allah.
The Sirat (Bridge)
All people will cross the Sirat — a bridge stretched over Hellfire, sharper than a blade and thinner than a hair. People will cross according to their light and deeds:
Believers will be saved by Allah’s mercy; wrongdoers will face consequences until He wills to forgive them.
Paradise (Jannah)
Paradise is the eternal home of joy, purity, and peace — prepared for the believers. Allah says: “No soul knows what delight of the eyes is kept hidden for them.” (Qur’an 32:17)
Rewards in Paradise
The Greatest Reward
The highest pleasure is seeing Allah’s Noble Face, as stated in the Qur’an (75:22–23) and Sahih Sunnah. The people of Paradise will have no greater joy than this moment.
Hellfire (Jahannam)
Hellfire is a real place of punishment, created by Allah for those who reject the truth and persist in sin. Its heat is immense — seventy times hotter than the fire of this world (Sahih al-Bukhari).
Levels of Punishment
Jahannam has levels, each with increasing severity:
Eternal or Temporary?
Allah says: “Indeed, whoever Allah admits to Paradise — He has shown him mercy.” (Qur’an 4:31)
Balance of Hope and Fear
A believer lives with a balanced heart — never despairing of Allah’s mercy and never feeling completely safe from His justice.
Allah praises those “who call upon their Lord in fear and hope.” (Qur’an 32:16)
Why Both Are Needed
Too much fear leads to hopelessness; too much hope leads to carelessness. Islam perfects the heart through balance.
Signs of the Hour
The Prophet ﷺ informed us of minor and major signs of the Last Day — so believers may remain mindful, not heedless. We affirm only what is authentic and avoid speculation.
Minor Signs
Major Signs (all authentically established):
Allah says: “The knowledge of the Hour is with Allah alone.” (Qur’an 31:34)
The signs remind us to prepare with righteous deeds, sincerity, and repentance.
How to Become a Muslim
Steps to Embrace Islam
Entering Islam is the most important and noble decision a person can make. Allah opens the heart of whomever He wills to the truth. The process is simple, clear, and rooted only in what Allah and His Messenger ﷺ taught.
1. Understand the Core Belief
Islam begins with firm conviction in the heart that:
This belief is the foundation of faith (Iman).
2. Declare the Testimony (Shahada)
A person becomes Muslim by sincerely saying: “Ashhadu an la ilaha illa Allah, wa ashhadu anna Muhammad an rasul Allah.” “I testify that there is no god worthy of worship except Allah, and I testify that Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah.”
The testimony must be spoken with understanding and sincerity — not out of pressure or formality.
3. Conditions of the Shahada
Classical scholars of Ahl al-Sunnah mention seven conditions:
These conditions help a new Muslim understand the weight and beauty of the declaration.
4. Repentance & A Fresh Start
The Prophet ﷺ said: “Islam wipes out what came before it.” (Sahih Muslim) All previous sins are forgiven. Your record is clean. You begin life anew — purified by Allah’s mercy.
5. Ghusl (Purification Bath)
It is recommended (mustahabb) to perform a full bath after embracing Islam. This symbolizes purification and beginning a new chapter.
6. Begin Praying Salah
Learning Salah (the five daily prayers) is the first major step after entering Islam:
7. Adopt a Halal Lifestyle
Islam transforms the heart and also the way we live:
Every change brings blessings and reward.
8. Seek Knowledge from Proper Sources
Knowledge is the light that guides the believer:
9. Connect With a Masjid & Righteous Companions
A good community keeps you firm and motivated:
10. Avoid Innovations (Bid‘ah)
Follow Islam as revealed:
This guarantees your practice remains pure, accepted, and safe from misguidance.
Next Steps & Support
Once you’ve embraced Islam, begin building a strong foundation with consistency and sincerity. Islam grows in the heart step by step.
1. Build Daily Habits
Small, consistent actions are beloved to Allah.
2. Read the Qur’an with Understanding
Use reliable tafseer such as:
Slowly study themes like Tawheed, Paradise, patience, and the lives of the prophets. The Qur’an becomes a personal guide for every moment of your life.
3. Attend Classes & Learn Gradually
Seek live or online lessons that follow Qur’an and Sunnah upon the understanding of the Salaf. Topics to prioritize:
Consistency brings clarity and strength.
4. Join Righteous Companions
The Prophet ﷺ said: “A person is upon the religion of his close friend.” (Tirmidhi — Hasan Sahih)
Being around good Muslims helps your heart grow, especially during challenges.
5. Make Du’a Often
Allah says: “Call upon Me; I will respond to you.” (Qur’an 40:60)
Ask Allah for guidance, strength, and ease. Du’a is your direct connection to Him, and He is near, forgiving, and merciful.
6. Be Patient & Celebrate Progress
Every new Muslim faces challenges — learning new habits, explaining your choice to family, or adjusting your lifestyle. Remember:
With sincerity, patience, and reliance on Allah, your faith will grow stronger each day.